Methane Production from Protozoan Endosymbionts Following Stimulation of Microbial Metabolism within Subsurface Sediments
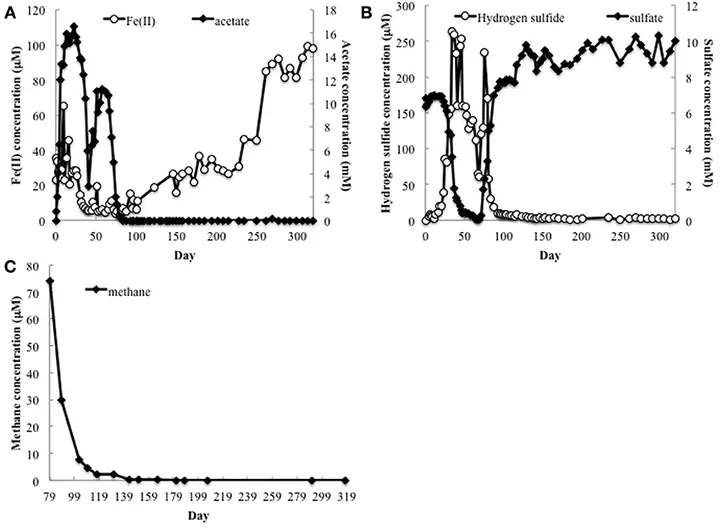 Image credit: [Lovley Lab]
Image credit: [Lovley Lab]Abstract
Previous studies have suggested that protozoa prey on Fe(III)- and sulfate-reducing bacteria that are enriched when acetate is added to uranium contaminated subsurface sediments to stimulate U(VI) reduction. In order to determine whether protozoa continue to impact subsurface biogeochemistry after these acetate amendments have stopped, 18S rRNA and ß-tubulin sequences from this phase of an in situ uranium bioremediation field experiment were analyzed. Sequences most similar to Metopus species predominated, with the majority of sequences most closely related to M. palaeformis, a cilitated protozoan known to harbor methanogenic symbionts. Quantification of mcrA mRNA transcripts in the groundwater suggested that methanogens closely related to Metopus endosymbionts were metabolically active at this time. There was a strong correlation between the number of mcrA transcripts from the putative endosymbiotic methanogen and Metopus ß-tubulin mRNA transcripts during the course of the field experiment, suggesting that the activity of the methanogens was dependent upon the activity of the Metopus species. Addition of the eukaryotic inhibitors cyclohexamide and colchicine to laboratory incubations of acetate-amended subsurface sediments significantly inhibited methane production and there was a direct correlation between methane concentration and Metopus ß-tubulin and putative symbiont mcrA gene copies. These results suggest that, following the stimulation of subsurface microbial growth with acetate, protozoa harboring methanogenic endosymbionts become important members of the microbial community, feeding on moribund biomass and producing methane.
Supplementary notes can be added here, including code and math.